Yoyo Math Vocabulary
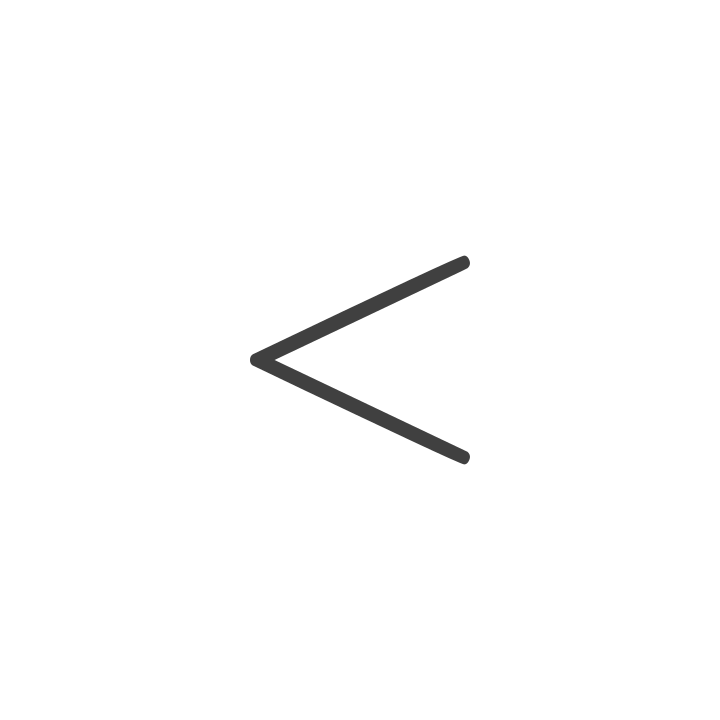
A symbol (<) used to compare two numbers when the first is smaller than the second.
A symbol (>) used to compare two numbers when the first is larger than the second.
The size, length, or amount of something, as established by measuring.
The result of adding two or more numbers together.
The result of subtracting one number from another.
Numbers that can be divided by 2 without a remainder (e.g., 2, 4, 6).
Numbers that cannot be divided by 2 without a remainder (e.g., 1, 3, 5).
The numerical value that a digit has by virtue of its position in a number.
The points where two or more edges meet in a geometric shape.
A balanced arrangement of elements on either side of a line or around a center.
A visual representation of data used to easily interpret information.
A diagram showing the relationship between variables, typically with axes.
Facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis.
A repeated or regular arrangement of elements in a set or sequence.
Counting forwards or backwards by a number other than one (e.g., by twos, fives, tens).
One of two equal parts of a whole.
One of three equal parts of a whole.
One of four equal parts of a whole.